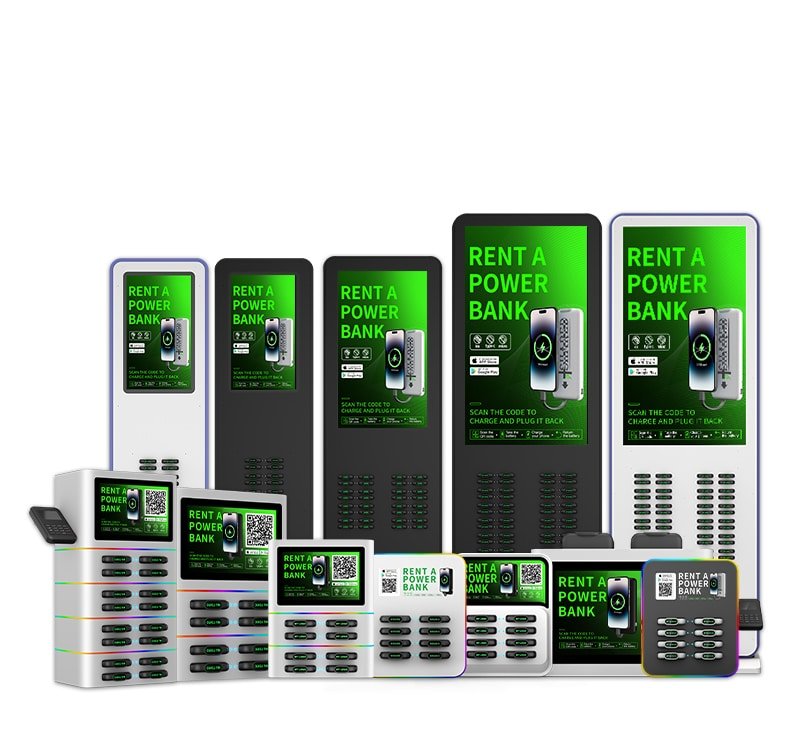
Power Bank Cabinet
Definition: The power bank cabinet is the core hardware facility of the shared power bank system, used for storing, charging, and managing multiple power bank devices. Cabinets are typically installed in commercial venues, allowing users to conveniently borrow and return power banks.
Location Selection: Cabinets can be selected and deployed in various high-traffic scenarios (such as restaurants, shopping malls, airports, and entertainment venues). The cabinet location directly affects user reach rate and usage frequency.
Operation Method: Remote monitoring of cabinet status through intelligent management systems, including power bank inventory, device health status, and transaction records. Operators can optimize cabinet layout and power bank configuration based on data analysis.
Charging Model
Definition: The charging model is the fee mechanism for shared power bank services, determining how users pay for usage fees.
Main Types: Includes time-based charging (hourly or minute-based fees), tiered charging (lower unit time prices for longer usage), and capped charging (setting daily maximum fee limits).
Implementation Method: Real-time settlement through mobile payment platforms; users can pay via QR code scanning or online account deduction. The system automatically records borrowing and returning times for precise fee calculation.
Scenario Coverage
Definition: Scenario coverage refers to the deployment range and density of shared power bank services in different usage environments.
Strategic Significance: Efficient scenario coverage can enhance brand visibility and user convenience, making it a key competitive indicator for operators.
Implementation Method: Determine high-frequency user activity areas through data analysis, establish strategic partnerships to expand service points, and adjust cabinet quantities and power bank configurations based on regional characteristics.
Operator
Definition: The operator is the business entity responsible for the operation, management, and maintenance of shared power bank businesses.
Scope of Responsibilities: Responsible for cabinet layout, power bank supply chain management, service quality monitoring, user experience optimization, and maintaining cooperation relationships with venue providers.
Profit Model: Achieves profitability through multiple channels including user rental fees, revenue sharing with venue merchants, advertising income, and data value.
Venue Provider
Definition: Venue providers are commercial entities that provide space for shared power bank cabinets, such as restaurants, shopping malls, hotels, etc.
Cooperation Model: Typically adopts a revenue-sharing model, where venue providers supply space and customer flow, operators provide equipment and operation maintenance, and both parties share revenue according to agreed proportions.
Selection Criteria: Ideal venue providers should have stable customer flow, longer dwell times, and suitable consumption scenarios to increase power bank usage rates.
Deposit System
Definition: The deposit system is a model where users need to pay a certain amount as a guarantee when first using a shared power bank service.
Implementation Method: Users pay a deposit before borrowing and can request a refund after returning the device. Deposits typically cover part or all of the power bank’s cost.
Industry Trend: With the development of credit systems and increased competition, the industry is gradually shifting toward deposit-free models to enhance user experience and convenience.
QR Code Rental
Definition: QR code rental is the process where users complete authentication, payment, and borrowing by scanning QR codes on cabinets or power banks.
Technical Implementation: Combines mobile payment platforms and shared power bank APPs or mini-programs to achieve rapid identity verification and transaction processing.
User Experience: Simplifies traditional rental processes; users only need a mobile phone to complete all operations, greatly enhancing convenience.
Light Operation
Definition: Light operation is an operational strategy adopted by the shared power bank industry featuring low manpower input and high automation.
Core Features: Achieves remote monitoring and management through intelligent systems, reducing manual inspection and maintenance frequency, and lowering operational costs.
Implementation Points: Relies on data analysis for location selection and replenishment decisions, establishes efficient logistics supplementary systems, and increases the number of devices managed per unit of manpower.
Capacity Level
Definition: Capacity level is the classification standard for measuring a power bank’s energy storage capability, typically in milliampere-hours (mAh).
Market Distribution: Common capacities in the shared power bank market range from 5000-10000mAh, satisfying one complete charging need.
Selection Strategy: Operators configure power banks of different capacity levels based on user dwell time and demand characteristics in different scenarios.
Fast Charging Technology
Definition: Fast charging technology enables charging devices at higher power, significantly reducing charging time.
Technical Parameters: Mainly includes output voltage, current, and power; common fast charging standards include QC and PD protocols.
User Value: Improves charging efficiency, reduces user waiting time, and is an important competitive indicator for shared power banks.
Conversion Rate
Definition: Conversion rate refers to the proportion of potential users who actually use the shared power bank service after seeing it.
Influencing Factors: Affected by various factors including price, convenience, brand trust, usage scenarios, and immediate needs.
Improvement Strategy: Enhance conversion rates by optimizing cabinet locations, simplifying operation processes, timely promotions, and increasing brand awareness.
Retention Rate
Definition: Retention rate refers to the proportion of users who continue to use the same brand of shared power bank after their first use.
Calculation Method: Usually calculated by day, week, or month to analyze the proportion of repeat users and evaluate user stickiness.
Improvement Means: Increase retention rates through membership systems, point rewards, multi-scenario coverage, and stable service quality.
Hotspot Layout
Definition: Hotspot layout is a strategy of increasing cabinet quantities and density in high-demand areas based on foot traffic and usage frequency.
Implementation Method: Reasonably plan cabinet quantities and distribution density based on big data analysis to identify users’ high-frequency activity areas.
Benefit Assessment: Measure hotspot layout effects through metrics such as output per unit area and cabinet saturation, with timely adjustments and optimization.
Intelligent Monitoring
Definition: Intelligent monitoring is a technical means of real-time data collection and status detection for shared power bank systems.
Monitoring Content: Includes various aspects such as power bank inventory, borrowing and returning records, charging status, fault warnings, and device safety.
Technical Implementation: Achieves remote real-time monitoring and intelligent decision support through Internet of Things technology, cloud platforms, and big data analysis.
Replenishment Strategy
Definition: Replenishment strategy is an operational plan for power bank allocation and updates based on cabinet usage rates and inventory status.
Decision Factors: Determines replenishment frequency and quantity based on historical data, usage peak periods, scenario characteristics, and seasonal changes.
Execution Method: Can adopt regular inspection replenishment, intelligent warning replenishment, or demand-driven replenishment modes to improve operational efficiency.
Single-Point Output Value
Definition: Single-point output value is an indicator measuring the economic benefit of each power bank cabinet, usually calculated as daily or monthly average revenue.
Influencing Factors: Affected by cabinet location, customer flow, consumption scenarios, pricing strategies, and operational levels.
Optimization Approach: Enhance single-point output value by optimizing cabinet locations, increasing turnover rates, reasonable pricing, and adding value-added services.
Market Penetration Rate
Definition: Market penetration rate refers to the proportion of people using shared power bank services in the target market.
Measurement Method: Estimate the usage proportion in specific regions or populations through user surveys, transaction data, and market observations.
Strategic Significance: High penetration rate indicates high market acceptance and user habit formation, an important indicator for evaluating industry development stages.
Multiple Interfaces
Definition: Multiple interfaces are the functional design of shared power banks equipped with various charging connectors to adapt to different devices.
Common Types: Include mainstream interfaces such as Type-C, Lightning, and Micro-USB to meet the needs of different brand devices.
Technical Advantages: Improves compatibility and ease of use; one power bank can meet the needs of multiple device users, enhancing the user experience.
Revenue-Sharing Ratio
Definition: Revenue-sharing ratio is the proportional relationship for dividing shared power bank income between operators and venue providers according to agreements.
Typical Models: Common ratios include 5:5, 6:4, or 7:3, determined based on each party’s input, resource value, and market conditions.
Influencing Factors: Affected by venue value, customer flow quality, market competition, and cooperation cycles; may be adjusted as cooperation deepens.
Platform Traffic
Definition: Platform traffic refers to the user visits and activity acquired through shared power bank APPs or mini-programs.
Value Manifestation: Beyond direct rental income, platform traffic can be converted into advertising value, membership services, and data assets.
Operational Strategy: Enhance platform attractiveness through marketing activities, user incentives, and functional optimization to cultivate user habits.
Safety Assurance
Definition: Safety assurance is a comprehensive measure ensuring the safety of shared power bank products and user data security.
Hardware Safety: Includes multiple hardware safety mechanisms such as overcharge protection, short-circuit protection, and overheating protection.
Data Security: Involves user payment information encryption, personal privacy protection, and transaction security.
Turnover Rate
Definition: Turnover rate is an indicator measuring the efficiency of shared power bank usage, representing the number of times each power bank is borrowed in a unit of time.
Calculation Method: Usually calculated daily or monthly; the calculation formula is the total number of borrowings in a specific time period divided by the number of available power banks.
Optimization Strategy: Improve turnover rate by optimizing cabinet locations, reasonably allocating power bank quantities, and enhancing service efficiency.
Dwell Time
Definition: Dwell time is the average duration users stay in a specific venue, directly affecting the demand and duration for shared power bank use.
Application Value: Helps operators evaluate scenario compatibility, predict usage duration and revenue, and optimize charging models.
Data Sources: Obtain dwell time data through user borrowing and returning records, venue customer flow analysis, and consumption behavior research.
Attrition Rate
Definition: Attrition rate refers to the proportion of asset reduction due to loss, damage, or aging of shared power banks during operations.
Control Methods: Reduce attrition rates through deposit mechanisms, device tracking, quality control, and regular maintenance.
Industry Benchmark: The industry average monthly attrition rate is typically controlled between 3%-5%, an important indicator for measuring operational efficiency.
Online Traffic Acquisition
Definition: Online traffic acquisition is a marketing method of attracting users to pay attention to and use shared power bank services through internet channels.
Main Channels: Includes various online touchpoints such as social media, search engines, payment platform entrances, and partner APPs.
Implementation Strategy: Enhance conversion effects through incentive measures such as coupons, first-time experience discounts, and membership privileges.
Scenario Marketing
Definition: Scenario marketing is a marketing strategy conducting targeted promotion and services based on user environment and demand characteristics.
Typical Scenarios: Includes different environments such as food and entertainment, commercial shopping, transportation hubs, educational institutions, and medical facilities.
Execution Points: Adjust service forms, pricing strategies, and promotional content according to scenario characteristics to increase user acceptance.
Warning Mechanism
Definition: Warning mechanism is a technical means for timely discovery and handling of abnormal conditions in shared power bank systems.
Warning Types: Includes various types such as inventory warnings, fault warnings, abnormal transaction warnings, and security risk warnings.
Response Process: Establishes a tiered response mechanism, initiating corresponding handling processes according to warning levels to ensure stable system operation.
User Profile
Definition: User profile is a data description of shared power bank users’ demographic characteristics, behavioral habits, and demand features.
Construction Dimensions: Includes dimensions such as age structure, usage frequency, average rental duration, preferred scenarios, and price sensitivity.
Application Value: Guides product optimization, precise marketing, and differentiated services to enhance user satisfaction and retention rates.
Platform Ecosystem
Definition: Platform ecosystem is a diverse value-added service and partner network built around the core service of shared power banks.
Components: Includes multiple entities such as payment platforms, venue partners, advertisers, hardware suppliers, and user communities.
Development Path: Evolves from a single rental service to a comprehensive service platform, expanding revenue sources and user value.
Smart Hardware
Definition: Smart hardware refers to shared power bank devices and cabinets with networking, data collection, and remote control capabilities.
Core Functions: Achieves efficient operational capabilities such as automatic identification, precise billing, remote monitoring, and intelligent management.
Technical Evolution: Develops from basic charging functions toward multi-functional integration, increasing payment convenience and user experience.
Data Assets
Definition: Data assets are valuable information accumulated during shared power bank operations, including user behavior, transactions, and locations.
Value Manifestation: Optimizes operational decisions and improves service quality through data analysis; can even serve as commercial resources for third-party cooperation.
Management Requirements: Must comply with data security and privacy protection regulations and establish a comprehensive data governance system.
Brand Matrix
Definition: Brand matrix is a strategy where large shared power bank enterprises operate multiple sub-brands to cover different market segments.
Strategic Significance: Meets the needs of different consumption scenarios and user groups, achieves full market coverage, and increases overall market share.
Management Challenges: Needs to balance resource allocation between brands, avoid internal competition, while maintaining each brand’s characteristics and competitiveness.
Cabinet Saturation
Definition: Cabinet saturation refers to the proportion of power banks already borrowed out of the total capacity in a power bank cabinet.
Application Scenario: Used to evaluate the reasonableness of cabinet capacity planning and guide replenishment decisions and resource allocation.
Optimization Interval: Ideal saturation is typically maintained between 60%-80%, ensuring sufficient supply while avoiding resource idleness.
Multi-Scenario Strategy
Definition: Multi-scenario strategy is the systematic planning of differentiated operational solutions for different usage environments by shared power bank enterprises.
Implementation Method: Adjusts cabinet types, power bank configurations, pricing strategies, and service content based on scenario characteristics.
Competitive Advantage: Improves users’ full-scenario service experience, enhances brand recognition and user stickiness, and increases market competitiveness.
Community Operation
Definition: Community operation is a marketing method that enhances user stickiness and brand interaction by establishing user communities.
Operation Means: Includes various methods such as membership privileges, point rewards, interactive activities, and user feedback mechanisms.
Value Contribution: Improves user retention rates, obtains product feedback, cultivates brand loyalty, and reduces customer acquisition costs.
Cyclic Supply
Definition: Cyclic supply is a logistics operation system ensuring adequate inventory and device status for shared power bank cabinets.
Implementation Process: Includes inventory monitoring, demand forecasting, route planning, equipment maintenance, and fault handling.
Optimization Goal: Minimizes operational costs while ensuring service quality, balancing resource utilization and user satisfaction.
Advertising Space Monetization
Definition: Advertising space monetization is a business model of obtaining revenue by displaying third-party advertising content on shared power bank cabinets and APP interfaces.
Value Proposition: High-frequency contact scenarios and precise user profiles make shared power banks an effective advertising medium.
Implementation Forms: Includes various forms such as cabinet screen advertising, power bank shell advertising, in-APP advertising, and scenario joint marketing.
Venue Rental Cost
Definition: Venue rental cost is the fee paid by shared power bank enterprises to venue providers for cabinet placement locations.
Calculation Method: Can adopt fixed rent, revenue sharing, or mixed models, determined based on venue value and cooperative relationships.
Control Strategy: Control venue rental cost rates through optimizing cabinet output, extending cooperation cycles, and providing value-added services.
User Experience
Definition: User experience is the comprehensive performance of shared power bank services in meeting user needs and comfort during the usage process.
Evaluation Dimensions: Covers aspects including acquisition convenience, operational simplicity, charging efficiency, price reasonableness, and problem-solving ability.
Improvement Methods: Continuously improve user experience through user research, interface optimization, process simplification, and service enhancement.
Customized Service
Definition: Customized service is the non-standardized exclusive service provided by shared power bank enterprises based on specific scenarios or customer needs.
Application Scenarios: Large events, enterprise customization, and special venues that require specific solutions.
Implementation Method: Can include exclusive appearance design, customized charging plans, and brand joint promotion in various forms.
Tiered Pricing
Definition: Tiered pricing is a charging strategy setting different price ranges based on usage duration, typically with decreasing unit time prices as usage time extends.
Implementation Method: Such as 10 yuan for the first hour, then 5 yuan per hour afterward, or setting package prices for different duration tiers.
Strategic Significance: Balances the charging reasonableness of short-time and long-time usage, improving user acceptance and satisfaction.
Asset Lifecycle
Definition: Asset lifecycle is the entire useful life period of a shared power bank from deployment to retirement.
Cycle Division: Includes introduction period, stable period, and decline period, with different management strategies adopted at different stages.
Extension Methods: Extend asset service life through quality control, regular maintenance, and reasonable usage frequency control to improve investment returns.
Cross-Region Borrowing and Returning
Definition: Cross-region borrowing and returning is a usage model where users borrow a power bank in one area and return it in another area.
Operational Challenges: Leads to power bank distribution imbalance, increasing allocation difficulties and operational costs.
Response Strategy: Balance resource distribution through differentiated charging, guiding nearby returns, or establishing allocation mechanisms.
Offline Touchpoints
Definition: Offline touchpoints are physical venues and equipment where users have tangible contact with shared power bank services.
Diverse Forms: Includes various forms such as standard cabinets, mini cabinets, front desk borrowing, and promotional points.
Optimization Approach: Improve touchpoint visibility, operational convenience, and brand recognition to enhance user conversion rates.
Capital Recovery Period
Definition: Capital recovery period is the time cycle required for shared power bank project investment costs to be fully recovered through operational revenue.
Calculation Method: Total investment divided by average monthly net income to obtain the estimated recovery months.
Industry Benchmark: The industry average capital recovery period is typically 12-18 months, affected by location, model, and operational efficiency.
High-Frequency Users
Definition: High-frequency users are user groups who use the same shared power bank brand service multiple times within a specific time period.
Value Manifestation: Contributes the main revenue source, provides stable cash flow, and is a core indicator of brand loyalty.
Cultivation Strategy: Increase the proportion and usage frequency of high-frequency users through membership systems, point rewards, and personalized services.
Traffic Conversion
Definition: Traffic conversion is the process of attracting potential users to shared power bank services and transforming them into actual users.
Conversion Funnel: Forms a complete conversion path from awareness, understanding, and trying to continuous use.
Optimization Means: Improve conversion efficiency by optimizing user interfaces, simplifying operation processes, and providing first-time experience discounts.
Regional Density
Definition: Regional density is the distribution concentration of shared power bank cabinets in a specific area, typically expressed as the number of cabinets per unit area.
Planning Principles: Determine optimal density based on foot traffic, consumption scenarios, and competitive conditions, avoiding excessive competition or service gaps.
Adjustment Strategy: Dynamically adjust regional layout based on usage data to improve resource utilization efficiency.
Industry Chain Integration
Definition: Industry chain integration is the strategic behavior of shared power bank enterprises controlling more industrial links through vertical or horizontal expansion.
Integration Direction: Includes multiple links such as upstream hardware manufacturing, midstream platform operation, and downstream scenario resources.
Value Creation: Reduces intermediate costs, improves supply chain efficiency, and enhances market bargaining power and risk resistance capability.
Equipment Standardization
Definition: Equipment standardization is the process of unified regulation of charging equipment interfaces, performance, and safety standards in the shared power bank industry.
Implementation Fields: Includes multiple aspects such as charging interfaces, battery capacity, charging protocols, and safety standards.
Industry Significance: Improves consistency of user experience, reduces manufacturing costs, and promotes healthy industry development.
Value-Added Services
Definition: Value-added services are additional service content provided by shared power bank enterprises beyond basic charging services.
Service Types: Includes various forms such as data cable sales, digital accessory rentals, advertising pushes, and coupon distribution.
Commercial Value: Expands revenue sources, enhances per-customer value, and strengthens competitive differentiation advantages.
Brand Penetration
Definition: Brand penetration is the process of increasing brand awareness and influence through multiple channels by shared power bank enterprises.
Implementation Paths: Includes multiple channels such as scenario coverage, media placement, user word-of-mouth, and industry cooperation.
Evaluation Indicators: Measures penetration effects through indicators such as brand awareness, mention rate, and preference rate.
Merchant Cooperation
Definition: Merchant cooperation is the long-term business cooperation relationship established between shared power bank enterprises and venue merchants.
Cooperation Models: Includes flexible forms such as revenue sharing, fixed rent, or service-for-location exchanges.
Maintenance Points: Provide stable service quality, maintain transparent settlement mechanisms, and create win-win value.
Technical Iteration
Definition: Technical iteration is the continuous process of functional updates and performance improvements for shared power bank equipment and systems.
Iteration Direction: Includes multiple aspects such as hardware performance improvement, software function enhancement, and user experience optimization.
Implementation Strategy: Regularly launch new versions of products and services based on user feedback and market demand.
Social Marketing
Definition: Social marketing is a marketing method of promoting shared power bank services using social media platforms and social relationship networks.
Implementation Channels: Includes mainstream social platforms such as WeChat, Weibo, Xiaohongshu, and TikTok.
Effect Enhancement: Amplify marketing effects and reduce customer acquisition costs through content creativity, user interaction, and social sharing.
Differentiated Competition
Definition: Differentiated competition is a strategy where shared power bank enterprises form market competitive advantages through unique product characteristics or service models.
Differentiation Establishment: Can establish differences in technological innovation, service experience, scenario coverage, or business models.
Continuous Evolution: Continuously adjust differentiation strategies to maintain competitive advantage sustainability with market changes.
Refined Operation
Definition: Refined operation is an operational method where shared power bank enterprises conduct detailed management and data-driven optimization of various business links.
Application Fields: Covers entire business processes including location selection and layout, inventory management, pricing strategies, and customer service.
Implementation Points: Establish comprehensive data collection and analysis systems to form closed-loop decision-making and continuous optimization mechanisms.
Business Ecosystem
Definition: Business ecosystem is a diversified cooperation partner and value-added service network built around the core business of shared power banks.
Ecosystem Composition: Includes multiple entities such as hardware suppliers, venue partners, advertising clients, and user communities.
Value Creation: Forms a systematic business network of resource complementarity and value co-creation to enhance overall competitiveness.
User Feedback Loop
Definition: User feedback loop is a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and responding to user opinions for continuous improvement of products and services.
Implementation Links: Includes links such as feedback collection, problem classification, solution formulation, and optimization implementation.
Value Manifestation: Improves user satisfaction, reduces churn rates, and guides product iteration and service optimization directions.